List of Equity Mutual Funds Schemes
Bajaj Finserv Small Cap Fund
Equity Fund Regular GrowthBajaj Finserv Multi Cap Fund
Equity Fund Regular GrowthBajaj Finserv ELSS Tax Saver Fund
Equity Fund Regular GrowthBajaj Finserv HealthCare Fund
Equity Fund Regular GrowthBajaj Finserv Consumption Fund
Equity Fund Regular GrowthBajaj Finserv Large Cap Fund
Equity Fund Regular GrowthBajaj Finserv Large and Mid Cap Fund
Equity Fund Regular GrowthBajaj Finserv Flexi Cap Fund
Equity Fund Regular GrowthWhat is an Equity Fund?
An equity fund is a mutual fund that invests primarily in the shares of listed companies. It collects money from multiple investors and allocates it across a portfolio of stocks with the objective of generating long-term capital growth. These funds are managed by professional fund managers and offer diversification by investing across different companies and sectors, which may help reduce the impact of individual stock movements. Equity funds are generally suitable to investors who are comfortable with market-linked volatility and are seeking potential capital appreciation over the long term. Equity mutual funds come in various forms, some focusing on a specific market capitalisation (such as large cap, mid cap or small cap funds), others investing in companies of all sizes (such as multi cap funds) and some focusing on specific sectors or themes.
How do Equity Funds Work?
Equity funds function through structured portfolio management, regulatory oversight, and market linked valuation, as outlined below:
- Pooling of investor money: Equity funds collect money from multiple investors and issue units based on the amount invested.
- Portfolio construction: The fund manager selects stocks based on the scheme’s investment objective and the scheme category. Some common sub-types of equity funds include large cap funds, small cap funds, flexi cap funds and sectoral funds.
- Active or passive management: Actively managed funds aim to generate returns above a benchmark index. Passive funds, such as index funds and ETFs, replicate a specific index.
- NAV calculation: The Net Asset Value (NAV) is calculated daily based on the market value of the portfolio after deducting expenses.
- Market-linked returns: Returns depend on stock price movements, corporate earnings, economic conditions, and market sentiment. There are no assured returns.
- Risk and volatility: Equity funds may experience price fluctuations, especially in the short term. A long investment horizon may help manage volatility but does not eliminate risk.
- Investment options: Investors may choose growth or IDCW payout options based on cash flow preferences.
Who should invest in equity mutual funds?
The following categories of investors may consider evaluating equity mutual funds:
- Investors with a very high risk appetite: Those who are comfortable with market fluctuations and possible capital volatility.
- Long term investors: Individuals potentially looking to build wealth over time, typically with an investment horizon of five years or more.
- Goal based investors: Those planning for long term goals such as retirement or children’s education, where growth potential over time is important.
- Investors seeking inflation adjustment: Equity exposure may provide potential returns that outpace inflation over extended periods, though not guaranteed.
- Diversified portfolio builders: Investors aiming to allocate a portion of their portfolio to growth-oriented assets alongside relatively stable assets such as debt funds.
- SIP investors: Individuals who prefer investing gradually through Systematic Investment Plans to manage market volatility over time.
What are the types of equity mutual funds?
SEBI categorizes equity mutual funds In India into several segments:
- Large cap funds: Invests in the top 100 companies by market capitalisation, known for their relative stability and lower risk. These funds allocate at least 80% of assets to large cap companies.
- Mid cap funds: Focuses on companies ranked from 101st to 250th by market capitalisation. They target younger companies with higher growth potential, allocating at least 65% of assets to mid-cap stocks.
- Small cap funds: Invests in companies ranked beyond the top 250 by market capitalisation, known for their higher risk and potential for substantial growth. These funds allocate a minimum of 65% of assets to small cap companies.
- Large and mid cap funds: These funds invest in both large and mid-sized companies, balancing stability with growth potential. They allocate at least 35% of assets to both large and mid-cap stocks.
- Flexi cap funds: Offers flexibility by investing across companies of all sizes based on market conditions. They invest a minimum of 65% in equity and equity-related instruments.
- Multi cap funds: Invests across large-cap, mid-cap, and small-cap stocks, providing a blend of stability, growth potential, and flexibility. These funds must invest at least 75% of assets in equity and equity-related instruments. Also, a minimum of 25% should be invested in equity instruments of large-cap, mid-cap and small-cap each.
- ELSS funds: ELSS funds are equity-oriented schemes that offer tax benefits under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act, 1961, under the old regime. They come with a mandatory three-year lock-in period.
- Thematic/sectoral fund: Such funds invest in one sector or a group of sectors linked by a scheme (such as healthcare, consumption, infrastructure etc). They generally have more concentrated portfolios than other equity fund categories and therefore carry higher risk.
Features and benefits of equity mutual funds
Key features include:
- High equity exposure: They invest predominantly in equities and therefore are linked to stock market movements.
- Professional management: Managed by fund managers who make portfolio decisions based on research and stated investment objectives.
- Diversification: Investments are spread across multiple companies and sectors, which may help manage company-specific risk.
- Liquidity: Most open-ended equity funds allow purchase and redemption requests on any business day, subject to cut-off times and in some cases, exit loads.
- Transparency: Portfolio disclosures and NAV are published periodically as mandated by SEBI.
Benefits include:
- Long-term growth potential: Equity exposure may support potential wealth creation over time.
- Compounding effect: Staying invested over long periods may enhance return potential through compounding.
- Inflation-beating return potential: Equity investments may generate potential returns that outpace inflation over extended periods.
- Flexibility: Systematic Investment Plans may help manage volatility and facilitate disciplined investing through staggered investments.
- Variety of categories: Investors may choose from large cap, mid cap, small cap, multi cap, flexi cap, sectoral funds, ELSS funds and more, based on goals and risk appetite.
Taxation rules of equity mutual funds
Understanding the tax implications of equity funds can help you plan and optimize your investments effectively. Here are the taxation details for different types of equity mutual funds:
- Income Distribution cum Capital Withdrawal (IDCW): IDCW includes dividends and capital gains distributed by mutual fund schemes. Dividends are added to the investor’s taxable income and taxed as per their income tax slab rate. Dividends exceeding Rs. 10,000 are subject to a standard TDS rate of 10%.
- Capital Gains Tax: Applicable selling mutual fund units at a profit:
- As of 2026, short-term capital gains (held for less than 12 months) from equity funds are taxed at 20%, plus applicable surcharge and cess.
- Long-term capital gains (held for 12 months or more) up to Rs. 1.25 lakh per year are tax-free. Gains exceeding this limit are taxed at 12.5%, plus applicable surcharge and cess.
How to Choose a Suitable Equity Mutual Fund?
To choose an equity mutual fund scheme that may be suitable for you, consider factors such as your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon. Since equity funds invest in shares of companies, they may offer the potential for long-term wealth creation but also carry higher market-related risks compared to debt-oriented funds. Reviewing aspects like the fund category, performance trends*, and expense ratio may help in making an informed decision. It is also advisable to review scheme-related documents and, if needed, consult a financial advisor to assess whether the scheme is suitable for your profile.
*Past performance may or may not be sustained in future.
Things to Consider While Investing in Equity Mutual Funds
Before investing in an equity fund, investors should conduct thorough research and consider the following factors:
- Investment objective: Assess whether the fund’s stated objective aligns with personal financial goals, such as long-term capital appreciation, income potential, or a combination of both.
- Time horizon: Equity mutual funds are generally suited for longer investment horizons. Investors may evaluate whether they can remain invested through market fluctuations to potentially benefit from long-term growth.
- Risk profile: Understanding personal risk tolerance is important, as equity funds are subject to market volatility. Different equity categories carry varying levels of risk based on market capitalisation and sector exposure.
- Fund performance: Reviewing historical performance over different market cycles may provide perspective on how the fund has behaved in the past. Historical returns should be assessed alongside benchmarks and peer funds, with the understanding that past performance may or may not be sustained in future.
- Fund manager experience: The experience and investment approach of the fund manager may influence portfolio construction and risk management. Investors may review the fund manager’s track record across equity portfolios.
- Portfolio diversification: Diversification across sectors, industries and market capitalisations may help manage concentration risk. Investors may review the portfolio composition to understand exposure levels.
- Capital gains tax on equity mutual funds: Tax treatment depends on the holding period and prevailing tax regulations. Investors may consider the impact of short-term and long-term capital gains tax while evaluating post-tax outcomes.
How to invest in equity funds?
- Step 1: Choose the investment mode
Decide whether to invest through a Systematic Investment Plan (SIP) for regular investing or a lumpsum contribution based on available funds and preferences. - Step 2: Select the equity fund
Review the scheme’s investment objective, portfolio, risk profile and historical information to identify an equity fund aligned with your goals. - Step 3: Complete KYC formalities
Ensure Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements are completed, as this is mandatory before investing in mutual funds. - Step 4: Decide the investment amount and tenure
Choose the amount, frequency and investment horizon based on cash flows and long-term financial objectives. - Step 5: Make the investment
You may invest online or offline, either directly through the fund house or via a registered mutual fund distributor. - Step 6: Review periodically
Track the investment periodically and review alignment with financial goals, risk appetite and market conditions.
Explore Equity Funds
| ELSS Tax Saver Fund | Healthcare Mutual Fund | Multi Cap Fund |
|---|---|---|
| Large and Mid Cap Fund | Small Cap Fund | Large Cap Fund |
| Consumption Fund | Flexi Cap Fund | Banking and Financial Services Fund |
Other Mutual Fund Types
| All Mutual Funds | Debt Funds | Hybrid Funds |
|---|---|---|
| Exchange Traded Fund Funds | Savings Plus | Index Funds |
Learn About Mutual Funds

Investing isn’t just about numbers,…

In today’s fast-paced consumerist…

When markets fluctuate significantly…

Gold has traditionally been used in…

Image for representation purposes…

Gold often draws attention when…

Of the almost 4 crore unique…

Traditional wisdom in the mutual…

Retail investors predominantly…

A common question among investors is…
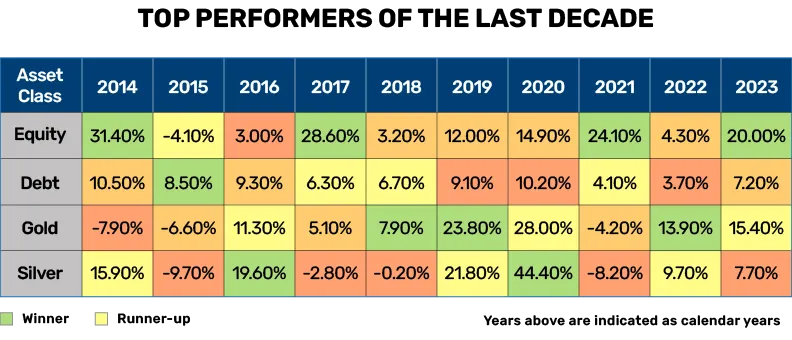
Equity, debt, gold, and silver have…

Recently, at a bustling farmers’…

Walk into your closet and take a…

You may not realise it, but when you…

Over the years, mutual funds have…

Planning for retirement involves…

Securing a comfortable post-…
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Equity mutual funds primarily invest in stocks or equities. These funds aim to achieve capital appreciation by investing in companies with growth potential or undervalued stocks.
Yes, equity funds carry a higher level of risk compared to debt funds due to the volatility of the stock market. They are subject to market fluctuations, economic conditions, and company-specific risks.
When selecting an equity fund, consider your investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. Look for funds with a consistent track record of performance, experienced fund managers, and a well-diversified portfolio aligned with your investment objectives. Conduct thorough research and seek professional advice if needed.
You can invest in equity mutual funds in India through SIP as well as lumpsum. SIP options can start as low as Rs. 500.
Equity mutual funds typically have a recommended investment horizon of at least 5 years or more. This longer timeframe helps to ride out market fluctuations and capture potential growth in stock prices.
Investing in equity funds in India can be beneficial for those seeking higher returns compared to traditional savings options like bank deposits. However, it involves market risks, so it's important for investors to have a long-term investment horizon and be prepared for fluctuations in value.
Equity refers to ownership in a company, typically through stocks, allowing direct exposure to stock market risks and returns. Mutual funds pool money from investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other assets, offering managed, lower-risk exposure than individual equity investments.
Equity mutual fund returns are subject to market risk and can fluctuate significantly from time to time. You can look at the past returns over three years, five years and longer intervals to get an idea of how much a scheme can potentially offer over multiple different market cycles. However, past performance may or may not be sustained in the future.
Equity funds tend to be volatile, especially in the short-term, and thus they may not be suitable for conservative investors and those with a low risk appetite. Such investors may consider debt mutual funds that offer relative stability and the potential for reasonable returns.
Neither is inherently better. Mutual funds offer diversification and professional management, which can mitigate risk and make investing accessible to beginners and those who do not have the expertise or time to track the markets. Direct equity carries higher risk but more control. It may be suitable for those who are familiar with the ins and outs of trading/investing and can control and manage their portfolios independently.
Yes, open-ended equity funds are generally liquid and you can redeem units when needed, but the value at redemption will depend on the prevailing Net Asset Value, which in turn depends on market conditions. Moreover, equity mutual funds are suitable for long-term investing, so it is advisable not to withdraw on impulse, as this may take you away from your goals. Lastly, capital gains on equity funds are taxable, so it is important to familiarise yourself with tax laws.
Cut-off time in mutual funds is the SEBI-specified time by which your purchase or redemption request must reach the fund house (subject to realization and availability of the funds in the bank account of mutual fund) to determine which day’s NAV will apply.
You may use online SIP calculators to estimate potential returns on your investment based on your investment amount, tenure and expected returns. However, the calculator’s estimates are for illustrative purposes only and actual returns will depend on market conditions – they are not fixed or guaranteed.
There is no fixed or universally suitable time to invest in an equity fund; the decision depends on your financial goals and investment horizon. Generally, the earlier you start, the more time your money gets to potentially grow through the power of compounding.
There is no single equity fund that may be considered ‘best’ for all investors. Suitability depends on individual factors such as financial goals, risk appetite, time horizon and market conditions.
Bajaj Finserv AMC’s equity fund offering continues to expand and currently includes funds such as the Bajaj Finserv Flexi Cap Fund, Bajaj Finserv Small Cap Fund, Bajaj Finserv Multi Cap Fund, Bajaj Finserv ELSS Fund, and Bajaj Finserv Banking and Financial Services Fund. You can find the latest and complete list of equity funds at the top of this page.
Equity funds include categories such as Large Cap Funds, Mid Cap Funds, Small Cap Funds, Flexi Cap Funds, ELSS Tax Saver Funds and sector or thematic funds.
Equity represents ownership in a company. For example, owning shares of a listed company gives the shareholder a proportional ownership interest in that business.
Equity funds may have an exit load, which is a charge applied if units are redeemed within a specified period. The amount varies by scheme and may be updated with time. You may the Scheme Information Document for details.
Investors may invest in equity funds through a Systematic Investment Plan (SIP) or a lumpsum amount, either online or offline, directly with the fund house or through a registered distributor.
Money may be withdrawn by placing a redemption request through the fund house’s website or an investment platform. The redemption amount is credited to the registered bank account, subject to applicable exit loads and processing timelines.
Mutual Fund Videos: Watch, Learn, Invest

Megatrends investing means looking…
Megatrends help anticipate the…
Megatrends investing focuses on long…

